Ranking
#28 on the list of 150 Most Teachable Lincoln Documents
Annotated Transcript
Audio Version
On This Date
HD Daily Report, September 15, 1858
The Lincoln Log, September 15, 1858
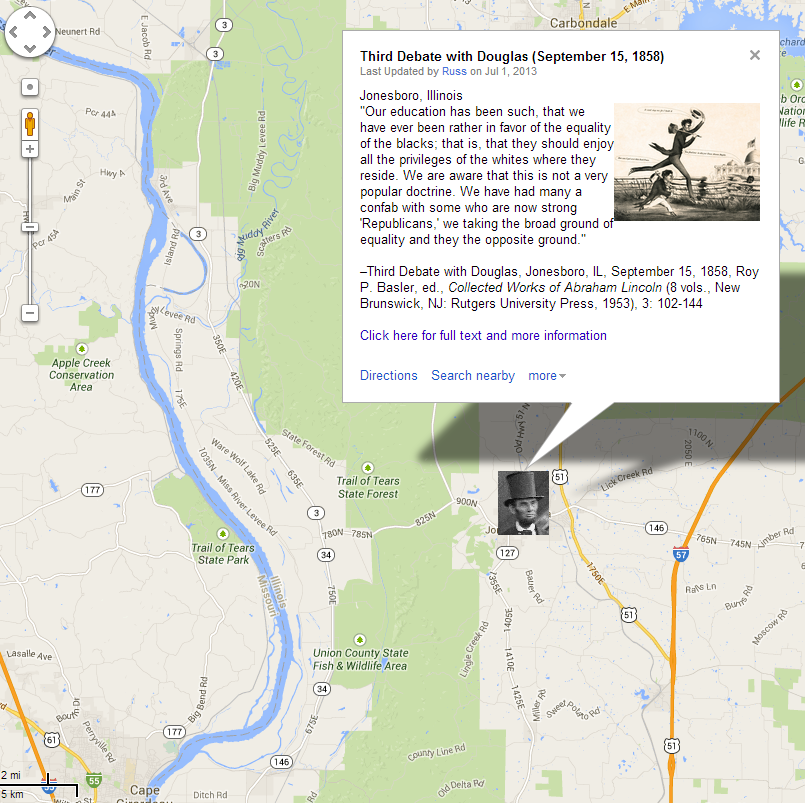
Custom Map
How Historians Interpret
“When Lincoln began his reply, he was ‘evidently embarrassed by the apparent uniform democratic hue of his audience.’ A faint cheer arose, ‘followed by derisive laughter from the Douglas men, and solemn silence from the ‘Danites.’’ Lincoln’s backers ‘took courage from this and burst into a loud cheer, which for the first time satisfied the statesmen on the platform, that matters were not all one way.’ Lincoln ‘proceeded in his accustomed sincere, earnest and good-humored way to present his side of the case.’ At first he was unimpressive, for ‘he began his address in a high-pitched, treble voice, all out of proportion to his massive head and frame, and accompanied it with rather an awkward carriage and gesture.’ One observer noted that ‘he got around about as gracefully as a woman climbs a rail fence,’ but another recalled that ‘as he warmed into his subject, I became unconscious of his appearance and his voice in the realization that I was listening to a wonderful message from a great soul.'”
“To his credit, Lincoln did not use his rebuttal to play to the prejudices of his listeners. He acknowledged that the audience contained few ‘political friends,’ but addressed the crowd respectfully as ‘intelligent people.’ He denied that he had every made a compact with cronies over mutual support for Senate seats. And he argued that Douglas’s popular sovereignty position was no longer viable under the Dred Scott ruling which made it impossible legally to bar slavery from new territories. Calling up ghosts of the heroes of the Revolution—still a potent political weapon in 1858—Lincoln asserted that the nation’s founders had laced slavery ‘on the course of the ultimate extinction.’ Douglas, he declared, was not thwarting their intentions. And he turned the tables on Douglas’s charges of ‘Black Republican’ abolitionist conspiracies by citing efforts by Illinois Democrats, some of whom Douglas had supported for election, to prevent the spread of slavery too.”
—The Lincoln-Douglas Debates: The First Complete Unexpurgated Text, Ed. Harold Holzer, (New York: Fordham University Press, 2004), 138.
NOTE TO READERS
This page is under construction and will be developed further by students in the new “Understanding Lincoln” online course sponsored by the House Divided Project at Dickinson College and the Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History. To find out more about the course and to see some of our videotaped class sessions, including virtual field trips to Ford’s Theatre and Gettysburg, please visit our Livestream page at http://new.livestream.com/gilderlehrman/lincoln
Searchable Text
LADIES AND GENTLEMEN: There is very much in the principles that Judge Douglas has here enunciated that I most cordially approve, and over which I shall have no controversy with him. In so far as he has insisted that all the States have the right to do exactly as they please about all their domestic relations, including that of slavery, I agree entirely with him. He places me wrong in spite of all I can tell him, though I repeat it again and again, insisting that I have no difference with him upon this subject. I have made a great many speeches, some of which have been printed, and it will be utterly impossible for him to find any thing that I have ever put in print contrary to what I now say upon this subject. I hold myself under constitutional obligations to allow the people in all the States, without interference, direct or indirect, to do exactly as they please, and I deny that I have any inclination to interfere with them, even if there were no such constitutional obligation. I can only say again that I am placed improperly-altogether improperly, in spite of all I can say-when it is insisted that I entertain any other view or purposes in regard to that matter.