Contributing Editors for this page include Adam Grant Kelley, Greg O’Reilly and Ben Widner
Ranking
#38 on the list of 150 Most Teachable Lincoln Documents
Annotated Transcript
“We meet this evening, not in sorrow, but in gladness of heart.”
Audio Version
On This Date
HD Daily Report, April 11, 1865
The Lincoln Log, April 11, 1865
Close Readings
Last.Speech from Adam Kelley on Vimeo with transcript available via Quora
Posted at YouTube by “Understanding Lincoln” course participant Greg O’Reilly, August 2014. Transcript available here.
Posted at YouTube by “Understanding Lincoln” course participant Ben Widner, August 2014
Custom Map
View in larger map
How Historians Interpret
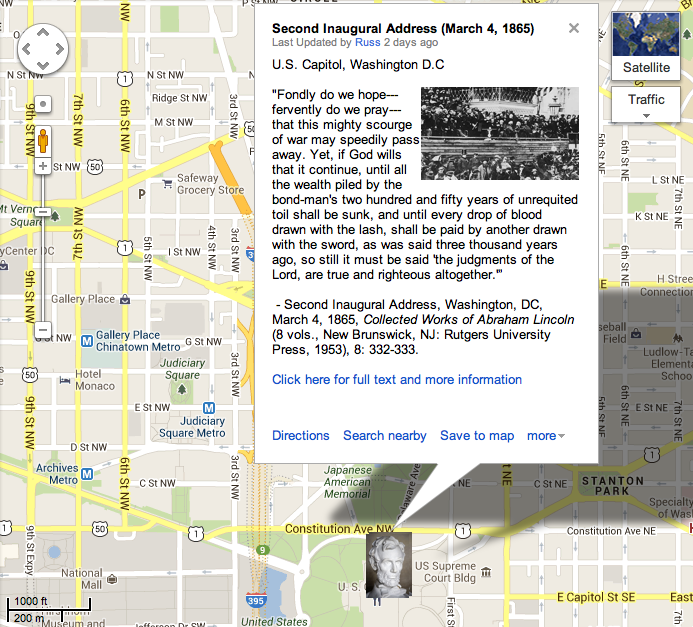
“On the misty evening of April 11, 1865, a huge crowd gathered on the north lawn of the White House and spilled out onto nearby streets to hear President Abraham Lincoln speak about the impending end of the Civil War. General Robert E. Lee had surrendered his army to General Ulysses S. Grant two days earlier. The Northern people had been celebrating ever since, and had not yet run out of energy. All Washington was ablaze with lights to herald the Union triumph. The festive throng expected a triumphant speech from the commander in chief whose armies had won the war. They should have known better. Lincoln was not given to exultant sentiments. He began with a brief reference to the satisfactions of victory and a call for national thanksgiving. But he quickly changed the mood by launching into a disquisition on the challenges of reconstructing a Union ravaged by four years of war. The crowd quieted. They showed a polite interest in the question of the future status of Louisiana and the other Confederate states now that the war was over, but that was not what they had come to hear. When the president expressed his preference that literate black men and those who served as Union soldiers should be granted the right to vote, some in the audience nodded in approval but others shook their heads in dissent.”
— Louis P. Masur, Lincoln’s Last Speech (New York: Oxford University Press, 2015), Xiii-xiv.
“In his last public address, on April 11, 1865, Lincoln referred to ‘the re-inauguration of the national authority—reconstruction.’ Although reluctant to use the term because it could imply that secession had destroyed the Union, Lincoln recognized the political reality of reconstruction, or reinauguration of national authority, throughout the war. He stated in his last speech that the subject of reconstruction ‘has had a large share of thought from the first.’”
— Herman Belz, “Lincoln’s Construction of the Executive Power in the Secession Crisis,” Journal of the Abraham Lincoln Association 27, no. 1 (2006): 12-38.
“Lincoln’s decision to undermine the radicals in Louisiana by calling for elections before a constitutional convention was not, McCrary argues, evidence of Lincoln’s conservatism but rather it was evidence that he had been badly misled by General Nathaniel P. Banks. At last, Lincoln recognized that Louisiana was headed in the wrong direction; he ‘came to recognize the fragile quality of the Hahn regime’s electoral support and became more comfortable with the prospect of Negro suffrage. As a pragmatic politician, if not as a man with a commitment to social justice for the freedmen, Lincoln could hardly have escaped the conclusion that at the end of the war there was nowhere to go but to the left.’”
— Arthur Zilversmith, “Lincoln and the Problem of Race: A Decade of Interpretations,” Journal of the Abraham Lincoln Association 2, no. 1 (1980): 22-45.
NOTE TO READERS
This page is under construction and will be developed further by students in the new “Understanding Lincoln” online course sponsored by the House Divided Project at Dickinson College and the Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History. To find out more about the course and to see some of our videotaped class sessions, including virtual field trips to Ford’s Theatre and Gettysburg, please visit our Livestream page at http://new.livestream.com/gilderlehrman/lincoln
Searchable Text
April 11, 1865
We meet this evening, not in sorrow, but in gladness of heart. The evacuation of Petersburg and Richmond, and the surrender of the principal insurgent army, give hope of a righteous and speedy peace whose joyous expression can not be restrained. In the midst of this, however, He, from Whom all blessings flow, must not be forgotten. A call for a national thanksgiving is being prepared, and will be duly promulgated. Nor must those whose harder part gives us the cause of rejoicing, be overlooked. Their honors must not be parcelled out with others. I myself, was near the front, and had the high pleasure of transmitting much of the good news to you; but no part of the honor, for plan or execution, is mine. To General Grant, his skilful officers, and brave men, all belongs. The gallant Navy stood ready, but was not in reach to take active part.
By these recent successes the re-inauguration of the national authority—reconstruction—which has had a large share of thought from the first, is pressed much more closely upon our attention. It is fraught with great difficulty. Unlike the case of a war between independent nations, there is no authorized organ for us to treat with. No one man has authority to give up the rebellion for any other man. We simply must begin with, and mould from, disorganized and discordant elements. Nor is it a small additional embarrassment that we, the loyal people, differ among ourselves as to the mode, manner, and means of reconstruction.
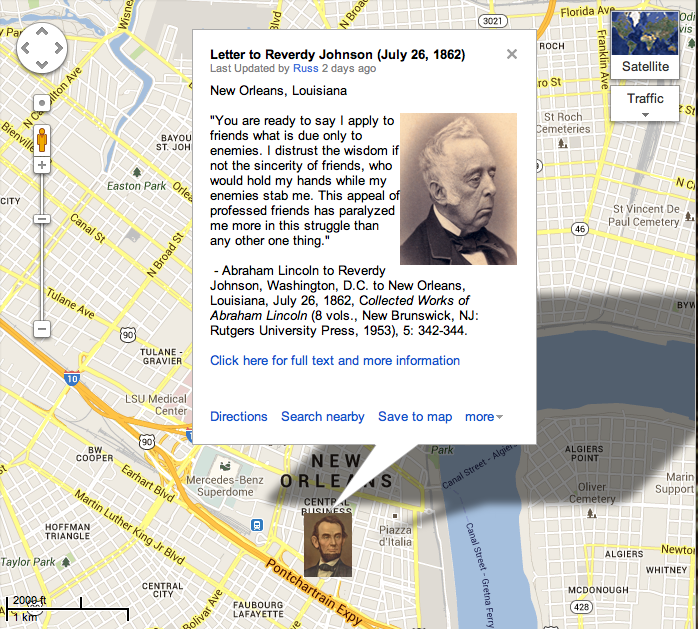
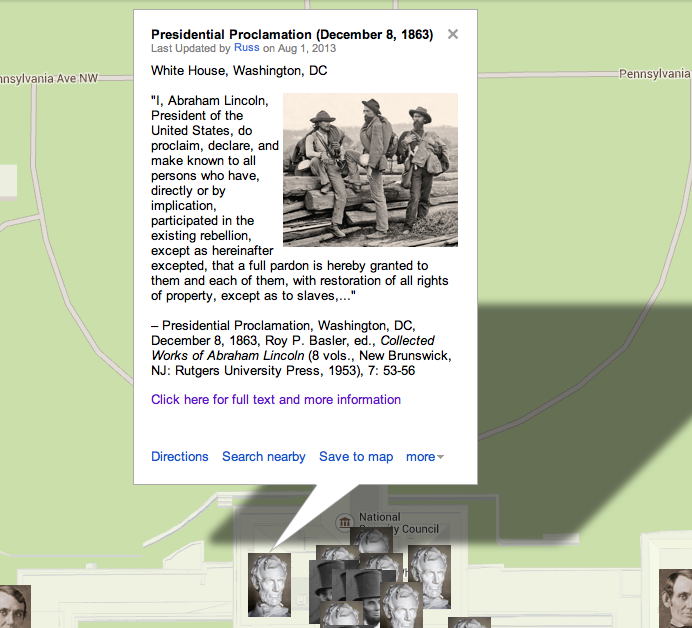
As a general rule, I abstain from reading the reports of attacks upon myself, wishing not to be provoked by that to which I can not properly offer an answer. In spite of this precaution, however, it comes to my knowledge that I am much censured for some supposed agency in setting up, and seeking to sustain, the new State Government of Louisiana. In this I have done just so much as, and no more than, the public knows. In the Annual Message of Dec. 1863 and accompanying Proclamation, I presented a plan of re-construction (as the phrase goes) which, I promised, if adopted by any State, should be acceptable to, and sustained by, the Executive government of the nation. I distinctly stated that this was not the only plan which might possibly be acceptable; and I also distinctly protested that the Executive claimed no right to say when, or whether members should be admitted to seats in Congress from such States. This plan was, in advance, submitted to the then Cabinet, and distinctly approved by every member of it. One of them suggested that I should then, and in that connection, apply the Emancipation Proclamation to the theretofore excepted parts of Virginia and Louisiana; that I should drop the suggestion about apprenticeship for freed-people, and that I should omit the protest against my own power, in regard to the admission of members to Congress; but even he approved every part and parcel of the plan which has since been employed or touched by the action of Louisiana. The new constitution of Louisiana, declaring emancipation for the whole State, practically applies the Proclamation to the part previously excepted. It does not adopt apprenticeship for freed-people; and it is silent, as it could not well be otherwise, about the admission of members to Congress. So that, as it applies to Louisiana, every member of the Cabinet fully approved the plan. The Message went to Congress, and I received many commendations of the plan, written and verbal; and not a single objection to it, from any professed emancipationist, came to my knowledge, until after the news reached Washington that the people of Louisiana had begun to move in accordance with it. From about July 1862, I had corresponded with different persons, supposed to be interested, seeking a reconstruction of a State government for Louisiana. When the Message of 1863, with the plan before mentioned, reached New-Orleans, Gen. Banks wrote me that he was confident the people, with his military co-operation, would reconstruct, substantially on that plan. I wrote him, and some of them to try it; they tried it, and the result is known. Such only has been my agency in getting up the Louisiana government. As to sustaining it, my promise is out, as before stated. But, as bad promises are better broken than kept, I shall treat this as a bad promise, and break it, whenever I shall be convinced that keeping it is adverse to the public interest. But I have not yet been so convinced.
I have been shown a letter on this subject, supposed to be an able one, in which the writer expresses regret that my mind has not seemed to be definitely fixed on the question whether the seceded States, so called, are in the Union or out of it. It would perhaps, add astonishment to his regret, were he to learn that since I have found professed Union men endeavoring to make that question, I havepurposely forborne any public expression upon it. As appears to me that question has not been, nor yet is, a practically material one, and that any discussion of it, while it thus remains practically immaterial, could have no effect other than the mischievous one of dividing our friends. As yet, whatever it may hereafter become, that question is bad, as the basis of a controversy, and good for nothing at all—a merely pernicious abstraction.
We all agree that the seceded States, so called, are out of their proper practical relation with the Union; and that the sole object of the government, civil and military, in regard to those States is to again get them into that proper practical relation. I believe it is not only possible, but in fact, easier, to do this, without deciding, or even considering, whether these states have even been out of the Union, than with it. Finding themselves safely at home, it would be utterly immaterial whether they had ever been abroad. Let us all join in doing the acts necessary to restoring the proper practical relations between these states and the Union; and each forever after, innocently indulge his own opinion whether, in doing the acts, he brought the States from without, into the Union, or only gave them proper assistance, they never having been out of it.
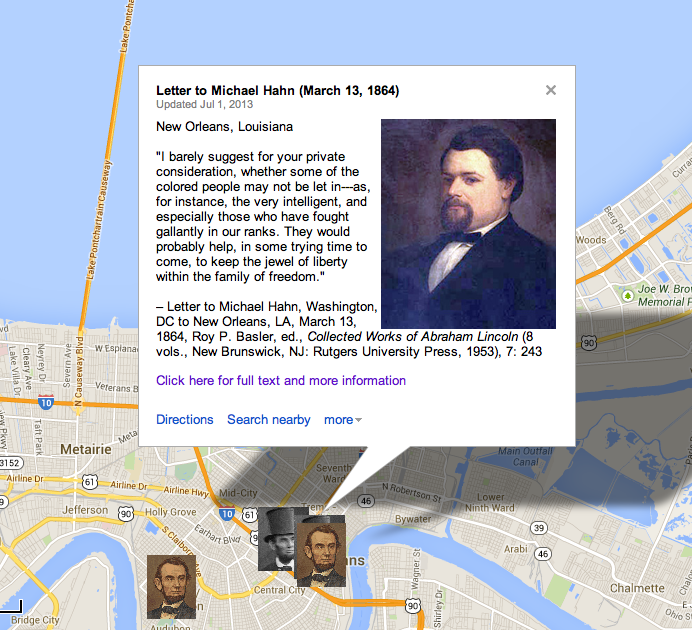
The amount of constituency, so to to [sic] speak, on which the new Louisiana government rests, would be more satisfactory to all, if it contained fifty, thirty, or even twenty thousand, instead of only about twelve thousand, as it does. It is also unsatisfactory to some that the elective franchise is not given to the colored man. I would myself prefer that it were now conferred on the very intelligent, and on those who serve our cause as soldiers. Still the question is not whether the Louisiana government, as it stands, is quite all that is desirable. The question is “Will it be wiser to take it as it is, and help to improve it; or to reject, and disperse it?” “Can Louisiana be brought into proper practical relation with the Union sooner bysustaining, or by discarding her new State Government?”
Some twelve thousand voters in the heretofore slave-state of Louisiana have sworn allegiance to the Union, assumed to be the rightful political power of the State, held elections, organized a State government, adopted a free-state constitution, giving the benefit of public schools equally to black and white, and empowering the Legislature to confer the elective franchise upon the colored man. Their Legislature has already voted to ratify the constitutional amendment recently passed by Congress, abolishing slavery throughout the nation. These twelve thousand persons are thus fully committed to the Union, and to perpetual freedom in the state—committed to the very things, and nearly all the things the nation wants—and they ask the nations recognition, and it’s assistance to make good their committal. Now, if we reject, and spurn them, we do our utmost to disorganize and disperse them. We in effect say to the white men “You are worthless, or worse—we will neither help you, nor be helped by you.” To the blacks we say “This cup of liberty which these, your old masters, hold to your lips, we will dash from you, and leave you to the chances of gathering the spilled and scattered contents in some vague and undefined when, where, and how.” If this course, discouraging and paralyzing both white and black, has any tendency to bring Louisiana into proper practical relations with the Union, I have, so far, been unable to perceive it. If, on the contrary, we recognize, and sustain the new government of Louisiana the converse of all this is made true. We encourage the hearts, and nerve the arms of the twelve thousand to adhere to their work, and argue for it, and proselyte for it, and fight for it, and feed it, and grow it, and ripen it to a complete success. The colored man too, in seeing all united for him, is inspired with vigilance, and energy, and daring, to the same end. Grant that he desires the elective franchise, will he not attain it sooner by saving the already advanced steps toward it, than by running backward over them? Concede that the new government of Louisiana is only to what it should be as the egg is to the fowl, we shall sooner have the fowl by hatching the egg than by smashing it? Again, if we reject Louisiana, we also reject one vote in favor of the proposed amendment to the national constitution. To meet this proposition, it has been argued that no more than three fourths of those States which have not attempted secession are necessary to validly ratify the amendment. I do not commit myself against this, further than to say that such a ratification would be questionable, and sure to be persistently questioned; while a ratification by three fourths of all the States would be unquestioned and unquestionable.
I repeat the question. “Can Louisiana be brought into proper practical relation with the Union sooner by sustaining or bydiscarding her new State Government?
What has been said of Louisiana will apply generally to other States. And yet so great peculiarities pertain to each state; and such important and sudden changes occur in the same state; and, withal, so new and unprecedented is the whole case, that no exclusive, and inflexible plan can safely be prescribed as to details and colatterals. Such exclusive, and inflexible plan, would surely become a new entanglement. Important principles may, and must, be inflexible.
In the present “situation” as the phrase goes, it may be my duty to make some new announcement to the people of the South. I am considering, and shall not fail to act, when satisfied that action will be proper.