Ranking
#104 on the list of 150 Most Teachable Lincoln Documents
Annotated Transcript
On This Date
HD Daily Report, January 14, 1863
The Lincoln Log, January 14, 1863
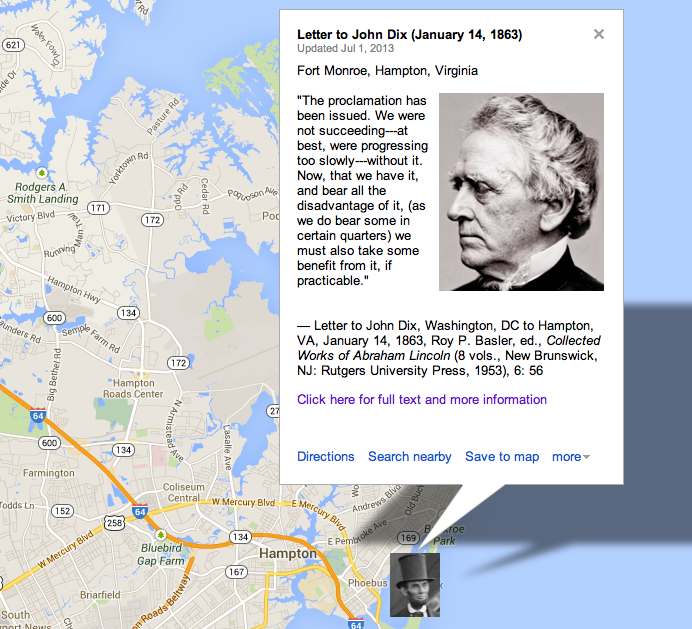
Custom Map
How Historians Interpret
“By spring the President was urging a massive recruitment of Negro troops. When neither General Butler not General Fremont accepted his offer to go South and raise a black army, Lincoln turned directly to men already in the field. ‘The colored population is the great available and yet unavailed of, force for restoring the Union,’ he reminded Andrew Johnson, whom he had appointed military governor of Tennessee, and he urged Johnson to take the lead in raising a force of black troops. ‘The bare sight of fifty thousand armed, and drilled black soldiers on the banks of the Mississippi,’ he predicted, ‘would end the rebellion at once.'”
–David Herbert Donald, Lincoln (New York: Simon & Schuster, 1995), 431
“Before he implemented his matured political strategy he moved to adopt a measure which was an extension and logical consequence of his Emancipation Proclamation. He announced that those blacks freed by the proclamation would ‘be received into the armed service of the United States to garrison forts, positions, stations, and other places.’ In this way Lincoln planned for manpower difficulties to be significantly eased by tapping this new source of soldiers, ‘the great available and as yet unavailed of, force for the restoration of the Union.’ Arming southern blacks most effectively harmonized with the basic anaconda strategy because Lincoln saw that it worked ‘doubly, weakening the enemy and strengthening us,’ for it took ‘so much labor from the insurgent cause, and supplying the places which otherwise must be filled with so many white men.’ Lincoln correctly believed that the program weakened the enemy in another way: psychologically. He thought that ‘the bare sight of fifty thousand armed, and drilled black soldiers on the banks of the Mississippi, would end the rebellion at once.’ He did not believe that the rebellion could survive if such a black military force could ‘take shape, and grow, and thrive, in the South.'”
“In justifying his hesitancy to endorse the recruitment of black troops and to issue the order of retaliation, Lincoln (according to Douglass) ‘said that the country needed talking up to that point. He hesitated in regard to it when he felt that the country was not ready for it. He knew that the colored man throughout this country was a despised man, a hated man, and he knew that if he at first came out with such a proclamation, all the hatred which is poured on the head of the negro race would be visited on his Administration. He said that there was preparatory work needed, and that that preparatory work had been done.’ He described that ‘preparatory work’ accomplished by black troops: ‘Remember this, Mr. Douglass; remember that Milliken’s Bend, Port Hudson, and Fort Wagner are recent events; and that these were necessary to prepare the way for this very proclamation of mine.’ If he had issued it earlier, he said, ‘such was the state of public popular prejudice that an outcry would have been raised against the measure. It would be said ‘Ah! We thought it would come to this. White men are to be killed for negroes.’'”
NOTE TO READERS
This page is under construction and will be developed further by students in the new “Understanding Lincoln” online course sponsored by the House Divided Project at Dickinson College and the Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History. To find out more about the course and to see some of our videotaped class sessions, including virtual field trips to Ford’s Theatre and Gettysburg, please visit our Livestream page at http://new.livestream.com/gilderlehrman/lincoln