Contributing Editors for this page include Jonas Sherr
Ranking
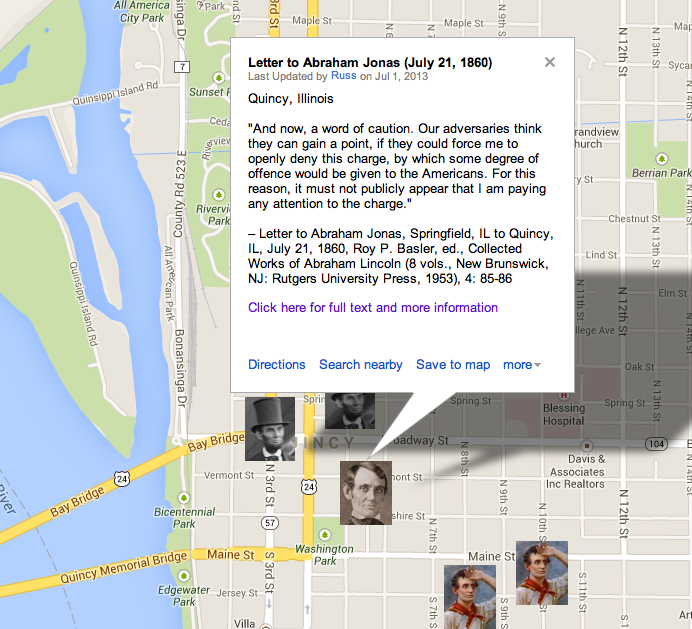
#144 on the list of 150 Most Teachable Lincoln Documents
Annotated Transcript
On This Date
HD Daily Report, July 21, 1860
The Lincoln Log, July 21, 1860
Close Readings
Jonas Sherr, “Understanding Lincoln” blog post (via Quora), Sep. 29, 2013
Custom Map
How Historians Interpret
“In 1860, Lincoln recalled his Quincy visit in a letter to Jonas: ‘It was in 1854, when I spoke in some Hall there, and after the speaking, you, with others, took me to, an oyster saloon, passed an hour there, and you walked with me to, and parted with me at, the Quincy-House, quite late at night. I left by stage for Naples before day-light in the morning, having come in by the same route, after dark, the evening previous to the speaking, when I found you waiting at the Quincy House to meet me…’ He went on to recall that it was this visit that led to a charge circulated by Congressman William A. Richardson that Lincoln had attended a Know-Nothing lodge in Quincy. Lincoln wanted to refute the allegation but without his personal involvement.”
–Lewis E. Lehrman, Lincoln At Peoria: The Turning Point (Mechanicsburg: Stackpole Books, 2008), 361.
“While it is possible to interpret these recollected accounts as confirmation that Lincoln resisted the Know-Nothings and saw himself primarily as a Whig, that interpretation would miss an important nuance. Lincoln opposed nativism but worked with nativists. In other words, the meeting itself had significance. What Lincoln avoided in 1854 was any open fusion between Whigs and Know-Nothings, which he feared would alienate strongly antislavery German immigrants such as George Schneider and potentially divide the opposition forces. As his concern about Benjamin Edwards and his discussion with Ballinger indicated, he certainly did not ignore the Know-Nothings who considered him an ally. Lincoln may have even accepted a secret arrangement with Know-Nothings but was at the very least willing to play down, or even abandon, his Whig identity in order to forge a broad-based coalition with them that might finally defeat the Democrats and, in particular, their statewide leader and his longtime nemesis, Senator Stephen Douglas.’
–Matthew Pinsker, “Not Always Such a Whig: Abraham Lincoln’s Partisan Realignment in the 1850s,” Journal of the Abraham Lincoln Association 29, no. 2 (2008): 27-46.
NOTE TO READERS
This page is under construction and will be developed further by students in the new “Understanding Lincoln” online course sponsored by the House Divided Project at Dickinson College and the Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History. To find out more about the course and to see some of our videotaped class sessions, including virtual field trips to Ford’s Theatre and Gettysburg, please visit our Livestream page at http://new.livestream.com/gilderlehrman/lincoln